Page 39 - Profile's Unit Trusts & Collective Investments - September 2025
P. 39
Basic concepts Chapter 2
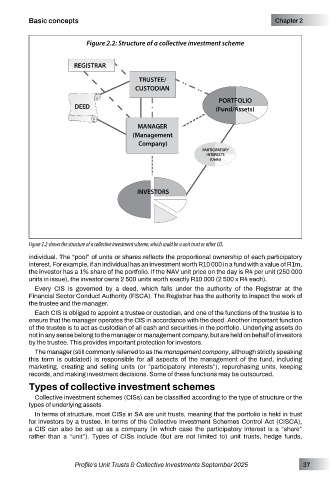
Figure 2.2: Structure of a collective investment scheme
REGISTRAR
TRUSTEE/
CUSTODIAN
PORTFOLIO
PORTFOLIO
und/Assets)
(F
(Fund/Assets)
MANAGER
(Management
Company)
Figure 2.2 shows the structure of a collective investment scheme, which could be a unit trust or other CIS.
individual. The “pool” of units or shares reflects the proportional ownership of each participatory
interest. For example, if an individual has an investment worth R10 000 in a fund with a value of R1m,
the investor has a 1% share of the portfolio. If the NAV unit price on the day is R4 per unit (250 000
units in issue), the investor owns 2 500 units worth exactly R10 000 (2 500 x R4 each).
Every CIS is governed by a deed, which falls under the authority of the Registrar at the
Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). The Registrar has the authority to inspect the work of
the trustee and the manager.
Each CIS is obliged to appoint a trustee or custodian, and one of the functions of the trustee is to
ensure that the manager operates the CIS in accordance with the deed. Another important function
of the trustee is to act as custodian of all cash and securities in the portfolio. Underlying assets do
not in any sense belong to the manager or management company, but are held on behalf of investors
by the trustee. This provides important protection for investors.
The manager (still commonly referred to as the management company, although strictly speaking
this term is outdated) is responsible for all aspects of the management of the fund, including
marketing, creating and selling units (or “participatory interests”), repurchasing units, keeping
records, and making investment decisions. Some of these functions may be outsourced.
Types of collective investment schemes
Collective investment schemes (CISs) can be classified according to the type of structure or the
types of underlying assets.
In terms of structure, most CISs in SA are unit trusts, meaning that the portfolio is held in trust
for investors by a trustee. In terms of the Collective Investment Schemes Control Act (CISCA),
a CIS can also be set up as a company (in which case the participatory interest is a “share”
rather than a “unit”). Types of CISs include (but are not limited to) unit trusts, hedge funds,
Profile’s Unit Trusts & Collective Investments September 2025 37